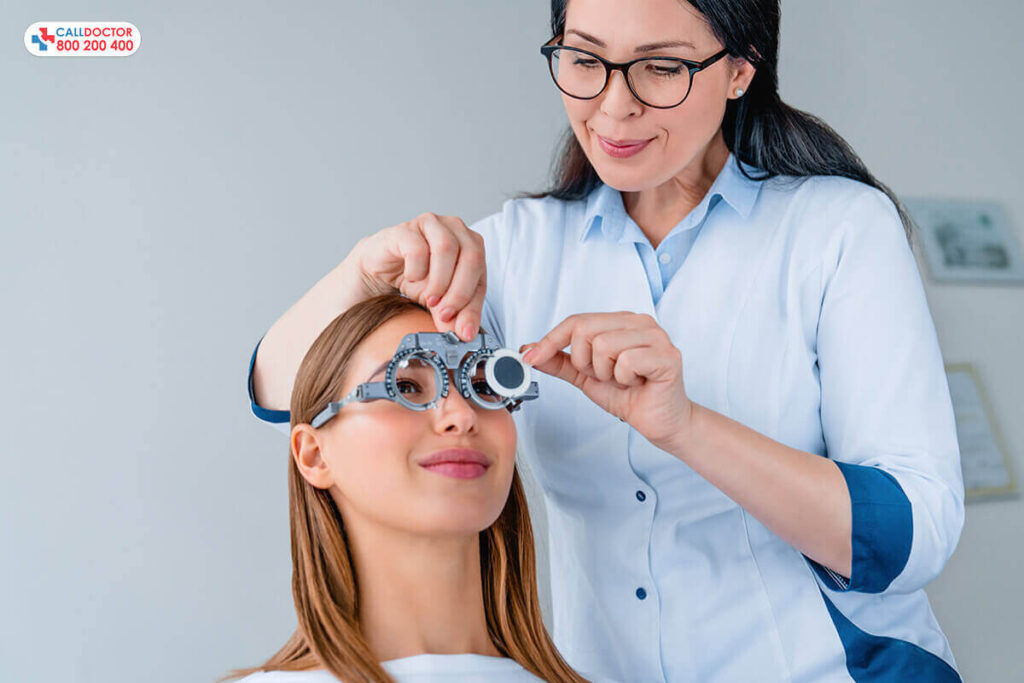
Vision, a precious gift often taken for granted, can be under siege by the silent culprit – Glaucoma. It is a term often heard but needs to be fully understood and poses a significant threat to vision. This blog will explore glaucoma treatments, types, causes, and proactive preventive approaches that can help combat this silent vision enemy.
Understanding Glaucoma
Glaucoma is not a singular condition but a group of eye diseases that can damage the optic nerve, leading to vision loss. It comes in various forms, including open-angle and angle-closure glaucoma, each with its characteristics and causes.
Recognizing Early Signs
Despite its prevalence, glaucoma often goes unnoticed until significant damage has occurred. Early detection is key. The common symptoms provide insights into how individuals can identify these signs early, seeking timely medical attention.
Here are some common Glaucoma symptoms:
Open-Angle Glaucoma
- Gradual loss of peripheral vision is often the first symptom; individuals may not notice the slow reduction in their side or peripheral vision.
- Tunnel vision is a condition that progresses; the visual field may narrow, resembling tunnel vision.
Closed-Angle Glaucoma (Acute Angle-Closure Glaucoma)
- Sudden and severe eye pain
- Headache and nausea
- Blurred or hazy vision
Normal-Tension Glaucoma
- Visual field changes are similar to open-angle glaucoma, and individuals may experience a gradual loss of peripheral vision.
- Optic nerve damage is the changes in the optic nerve that may be detected during an eye examination.
It’s important to note that glaucoma progresses without noticeable symptoms in many cases, highlighting the critical role of regular eye examinations, especially for individuals at risk.
Early detection and intervention can help prevent vision loss associated with glaucoma. If you experience any concerning changes in your vision or have glaucoma risk factors, consult an eye care professional for a thorough examination.
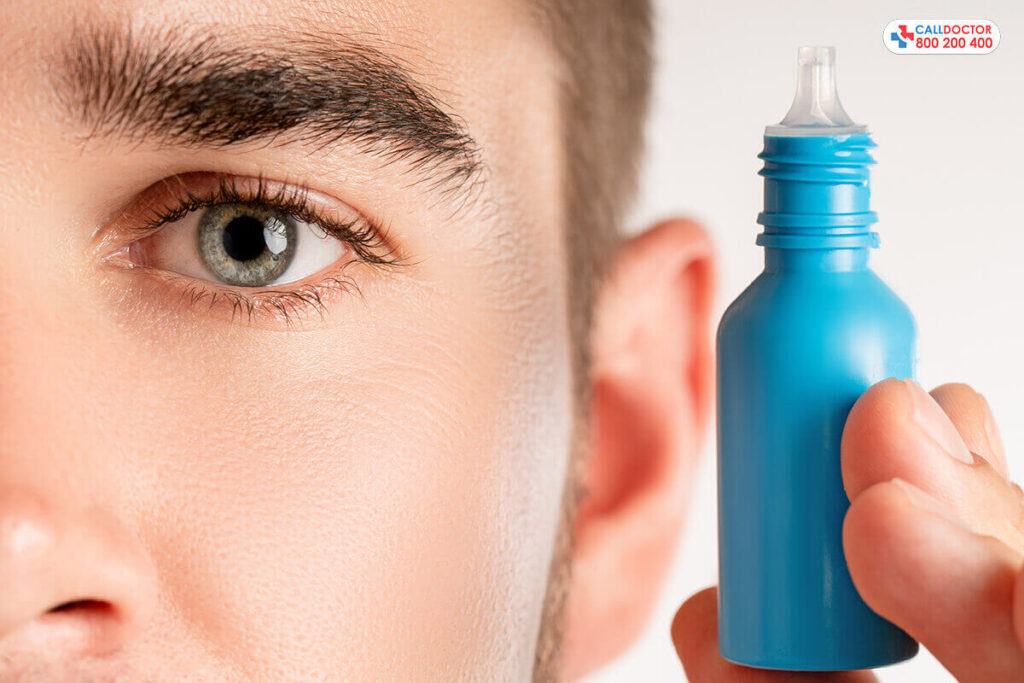

Risk Factors and Vulnerabilities
Certain given risk factors increase the chance of developing glaucoma, including,
- Age (60 years and older)
- Family history of glaucoma
- Elevated intraocular pressure (IOP)
- Thin central corneal thickness
- History of eye injuries or surgeries
- Use of corticosteroid medications
- Certain medical conditions (hypertension, diabetes)
- Severe nearsightedness or farsightedness
- Previous history of optic nerve abnormalities
Impact on Quality of Life
Beyond the physical implications, glaucoma can significantly impact everyday life and activities. Here are some key areas where glaucoma can influence an individual’s quality of life:
Visual Impairment
- Gradual loss of peripheral vision can lead to difficulties navigating surroundings, increasing the risk of accidents and falls.
- Tunnel vision in advanced stages may further limit the ability to perceive the full visual environment.
Independence and Mobility
- Reduced visual field and impaired depth perception can hinder independent mobility, making driving, walking, and using stairs more challenging.
Emotional Well-being
- Coping with the fear of vision loss and the impact on daily activities can lead to increased stress, anxiety, and a sense of isolation.
- Adjusting to lifestyle changes and relying on others for assistance may contribute to emotional distress.
Social Interaction
- Limited visual function may affect social interactions, making recognizing faces difficult and engaging in group activities challenging.
- The fear of being a burden to others may impact social participation.
Occupational Challenges
- Visual limitations may impact job performance, affecting tasks that require detailed vision or specific graphic skills.
- Individuals may face challenges in adapting to workplace conditions and accommodations.
Diagnostic Procedures
Knowledge is power. Understand the various diagnostic tests and procedures essential for identifying and confirming the presence of glaucoma. These three procedures play a vital role.
Tonometry
Measures intraocular pressure (IOP) to assess the risk of glaucoma. Elevated IOP is a key factor in glaucoma development.
Ophthalmoscopy
It examines the optic nerve head to detect signs of damage or changes, such as cupping or thinning, which may indicate glaucoma.
Visual Field Testing
This procedure evaluates the peripheral vision to identify abnormalities or loss, a common indicator of glaucoma. Performed using automated or manual techniques.
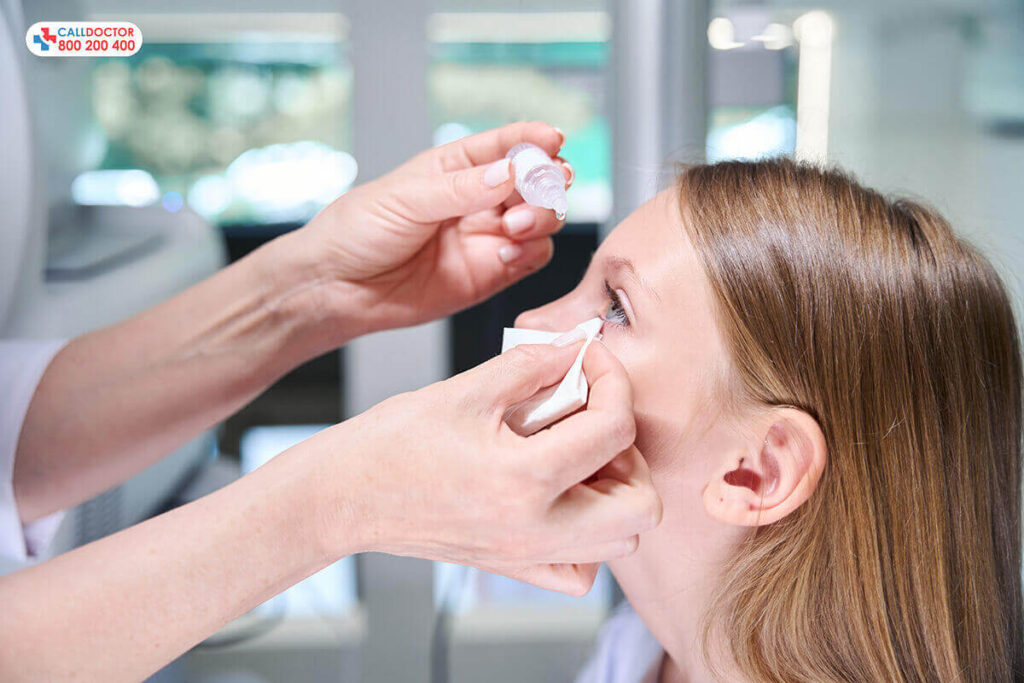
Current Treatment Options
The current treatment options for glaucoma aim to manage intraocular pressure (IOP) and prevent further optic nerve damage. The choice of treatment depends on the type and severity of glaucoma. Here are common treatment approaches:
Medications
Eyedrops
Eyedrops work by either reducing the production of aqueous humor or improving its drainage.
Oral Medications
Occasionally, oral medications may be prescribed to complement or replace eyedrop therapy. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and beta-blockers are examples.
Laser Therapy
Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty (SLT)
It uses laser energy to target specific cells in the trabecular meshwork, facilitating better drainage of aqueous humor and reducing IOP.
Laser Peripheral Iridotomy (LPI)
It addresses narrow-angle or closed-angle glaucoma by creating a small hole in the iris, allowing better fluid flow.
Surgical Procedures
Trabeculectomy
Creates a new drainage channel to enhance fluid outflow and lower IOP.
Minimally Invasive Glaucoma Surgery (MIGS)
Includes various procedures that aim to reduce IOP with minimal trauma and faster recovery compared to traditional surgeries.
Drainage Implants
Glaucoma Drainage Devices (GDDs)
Implanted devices provide an alternative pathway for aqueous humor drainage, reducing IOP.
Combination Therapy
Some patients may require a combination of medications, laser therapy, or surgery to manage glaucoma and maintain stable IOP effectively.
Individuals diagnosed with glaucoma must work closely with their eye care professionals to determine the most suitable treatment plan. Regular monitoring and adjustments to the treatment approach are standard to ensure optimal condition management and preservation of vision.
1. Can glaucoma be cured?
Glaucoma is a chronic condition, but early detection and management can prevent further vision loss.
2. Are there natural remedies for glaucoma?
While lifestyle changes can help manage glaucoma, they are not a substitute for medical treatment.
3. How often should I have an eye check-up to detect glaucoma early?
Annual eye examinations are recommended, especially for individuals over 40 or with risk factors.
4. Can glaucoma be hereditary?
A family history of glaucoma increases the risk, emphasizing the importance of regular check-ups.
5. Are there specific foods that can help prevent glaucoma?
A diet rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamins A, C, and E may contribute to eye health.
6. Can glaucoma affect children?
While rare, glaucoma can occur in children. Regular pediatric eye exams are essential for early detection.

Transform Your Eye Health with Call Doctor in Dubai!
A step towards a more precise vision is essential. Achieve it by scheduling your eye check-up with a Call Doctor. Moreover, you can preserve your eyesight and benefit from advanced screenings, expert consultations, and personalized care plans. Our convenient services ensure a hassle-free experience, whether on-site or at home. Don’t compromise on your eye health – contact Call Doctor today and prioritize the well-being of your vision. Your eyes deserve the best care; we’re here to provide it!